Introduction
The diagnosis of stomach cancer (or gastric cancer) is terrifying, and yet, right alongside the fear for your health and future comes another, often unspeakable anxiety: the financial cost. You are looking for treatment options, and like many thousands of people worldwide, you are exploring medical tourism. You must have seen the headlines: "Save 70% on Cancer Care!" This gets you intrigued, hopeful, but also utterly overwhelmed by the numbers. This guide is written with the understanding that you are a human being making one of the most significant decisions of your life. You will have a clear view of the costs, understanding the numbers and the true expense of seeking world-class stomach cancer care outside your country.
Why the Price Tag is So Elusive: The Variables That Change Everything
If you call five different hospitals today, you will get five wildly different price estimates, even for the same procedure. Why? Because stomach cancer treatment is not like buying a car, it is a bespoke, personalized medical journey. A dozen factors influence the final bill.
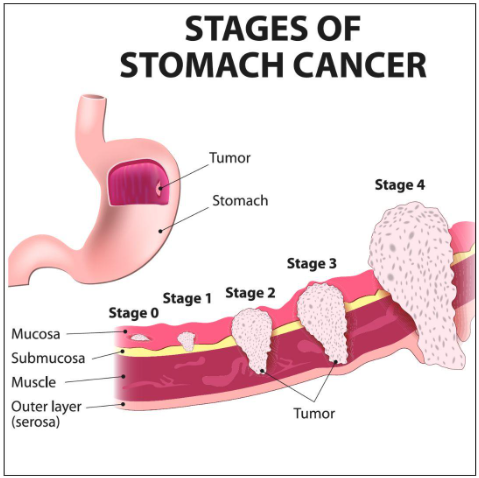
A. The Most Critical Factor: The Cancer Stage
The most dramatic variable affecting cost is how advanced the cancer is (the stage). It dictates the entire treatment strategy.
| Cancer Stage | Typical Treatment Plan | Financial Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Stage 0 (Early) | Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) or Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD). | Minimal. Often, a single, minimally invasive procedure. |
| Stage I & II (Localized) | Surgery (Gastrectomy), often followed by chemotherapy or chemoradiation. | Moderate to High. Involves a major surgery and several cycles of systemic therapy. |
| Stage III (Regional Spread) | Complex, multi-modal: Neoadjuvant chemo (before surgery), extensive surgery, and adjuvant chemo/radiation (after surgery). | High. Requires multiple medical disciplines and prolonged, expensive drug cycles. |
| Stage IV (Metastatic) | Primarily systemic therapy (Chemo, Targeted Therapy, Immunotherapy) and palliative surgery/procedures. | Very High (Long-term). Requires long-term, continuous, and often extremely expensive drug therapy. |
Takeaway: If you have Stage I cancer, the bulk of your cost is the surgery. If you have Stage IV, the surgery might be small (or non-existent), but the cost of the cutting-edge drugs for immunotherapy or targeted therapy will dominate the bill and continue for months or years.
B. The Surgical Details
For Stages I–III, surgery is the cornerstone of treatment. This is often the largest expense in your treatment plan.
- Type of Gastrectomy: A Partial Gastrectomy (removing only part of the stomach) is less complex and often cheaper than a Total Gastrectomy (removing the entire stomach and reconnecting the esophagus to the small intestine).
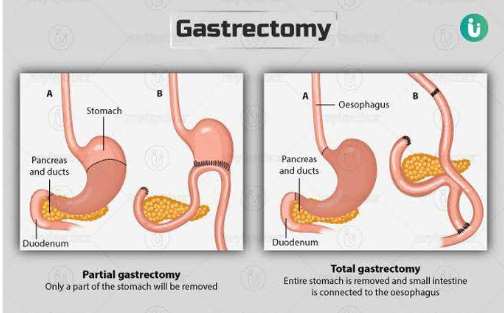
- Surgical Technique: A traditional Open Surgery is usually the lowest cost. A Laparoscopic (Keyhole) Gastrectomy costs more because it requires specialized equipment, but recovery is faster. A Robotic (Da Vinci) Gastrectomy is the most expensive robotic system rental and maintenance fees are passed on to the patient, but it offers the highest precision.
- Lymph Node Dissection (D2 Dissection): A standard part of curative gastric surgery, removing nearby lymph nodes to check for spread. The complexity and time involved factor heavily into the surgeon's fee.
C. The Cost of Modern Medicine: Drugs and Technology
This is where medical tourism savings can be both significant and deceptive.
- Chemotherapy: The cost depends entirely on the regimen. A standard, older regimen (like FOLFOX) is relatively affordable. A newer, taxane-based drug or a double/triple-agent therapy will be dramatically more expensive.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs like Trastuzumab (Herceptin) for HER2-positive tumors can be incredibly effective but carry a steep price tag, often running thousands of dollars per infusion.
- Immunotherapy: The newest frontier. Drugs like Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) or Nivolumab (Opdivo) use the body's immune system to fight cancer. These are game-changers, but they are often the most expensive cancer drugs in the world. If your treatment includes immunotherapy, it will be the single greatest long-term financial drain.
- Special Procedures (HIPEC): Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy is a procedure where heated chemotherapy is washed through the abdomen during surgery. It is highly specialized and one of the most expensive surgical treatments for advanced abdominal cancers.
Medical Tourism vs. Local Care: The Financial Gap
The primary reason patients travel is simple: cost savings without sacrificing quality. For stomach cancer, the savings are significant, particularly when comparing self-pay rates in the US to all-inclusive packages in Asia or Eastern Europe.
A. The Global Snapshot: Estimated Starter Prices
The table below shows the base price range for a major stomach cancer operation (e.g., Total Gastrectomy with D2 dissection) in an internationally accredited facility. These are just starting points and do not include systemic drug costs.
| Country | Estimated Range (USD) | Why the Price Difference? |
|---|---|---|
| USA (Self-Pay/Uninsured) | $80,000 – $180,000+ | High administrative costs, malpractice insurance, and a profit-driven health system. |
| Germany | $35,000 – $60,000 | High operational costs, highly specialized personnel, and top-tier technology. |
| South Korea | $25,000 – $45,000 | Government subsidies and high-volume, standardized procedures, particularly for gastric cancer. |
| Turkey | $18,000 – $35,000 | Favorable exchange rates, a competitive market, and a focus on high-quality JCI-accredited care. |
| India | $7,000 – $15,000 | Low labor and operating costs, high-volume practice, and an established medical tourism infrastructure. |
Takeaway: The difference is real. Traveling to a country like India or Turkey can literally save you the price of a second home. This saving is critical for funding the expensive, ongoing drug treatments that follow surgery.
B. Hidden Costs: The "Total Trip" Expense
When planning a journey to another country for cheaper treatment, patients often forget to add certain expenses which can eventually affect their total budget, such as:
- Travel and Logistics: Round-trip flights for the patient and a caregiver.
- Accommodation: Expect to be abroad for several weeks, if not months. This means paying for a hotel or rental apartment near the hospital.
- Caregiver Costs: The cost of food, local transportation.
- Visa and Insurance: Fees and the cost of specialized medical tourism insurance (highly recommended).
- Rehabilitation and Nutrition: Post-gastrectomy, you will need specialized care, nutritional support (often liquid/tube feeding initially), and possibly a translator for local follow-up visits.
The Detailed Cost Breakdown
Let’s understand the cost of your treatment with an example of the most common gastric cancer.
Example Patient Profile: 55-year-old male with Stage IIB Gastric Adenocarcinoma requiring Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy (chemotherapy before surgery to decrease the size of the tumor), Total Gastrectomy, and Adjuvant Chemotherapy.
| Treatment Cost Components (Example for Turkey/India Range) | Cost Range (USD) | Inclusions/Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic Workup (Pre-Travel) | $1,500 – $4,000 | CT Scan, Endoscopy/Biopsy review, Lab Tests, Oncologist Consult. (Can often be done locally). |
| Surgical Procedure (Total Gastrectomy) | $12,000 – $25,000 | Surgeon's fee, anesthetist, 7–10 days hospital stay, ICU time, supplies, operating room fee. |
| Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy (3 Cycles) | $4,500 – $15,000 | Cost of drugs, infusion center fees, and consulting oncologist fees for the pre-surgery period. |
| Adjuvant Chemotherapy (3–5 Cycles Post-Surgery) | $6,000 – $25,000 | Continuation of drug therapy after recovery. (Most variable cost). |
| Follow-Up & Palliative Care | $1,000 – $5,000 (Per Year) | Blood tests, imaging scans, nutritional support, and ongoing medication management. |
| Non-Medical/Logistics (3–4 weeks) | $3,000 – $7,000 | Flights, local accommodation, food, local transport, and travel insurance for the patient and companion. |
| Estimated TOTAL Package Cost | $27,000 – $81,000+ | This total can be significantly lower than the cost of surgery alone in a Western nation. |
The Critical Nuance: Immunotherapy Cost
If your cancer requires immunotherapy, the cost structure is completely different. A single dose of a major immunotherapy drug can cost $5,000 to $15,000 USD in many countries. If a patient needs 12 to 24 cycles over a year or two, the total cost for drugs alone can easily exceed $100,000 USD.
If you are traveling to save money, always inquire about:
- The availability of generic or biosimilar drugs in that country.
- The possibility of receiving initial cycles abroad and then safely purchasing and transporting medication home (if legally permissible).
- The hospital’s "package deal" for an entire year of systemic therapy can offer a better price than paying per cycle.
Your Action Plan: Getting a Clear Quote
Don’t accept a vague estimate. A quality medical tourism provider or hospital should be able to offer a comprehensive "all-inclusive" quote based on your specific staging reports.
What your quote must include:
- Diagnosis and Staging: All required pre-treatment blood work, scans (CT, PET, EUS), and pathology review.
- Surgery: A clear statement of the type of gastrectomy (partial/total, laparoscopic/robotic), the surgeon's name and credentials, and the expected length of hospital stay (including ICU if necessary).
- Systemic Therapy: The name of every chemotherapy, targeted, or immunotherapy drug you will receive, the number of cycles included, and the cost per cycle.
- Post-Operative Care: Details on medications for pain and nutritional recovery, and the number of follow-up consultations included before discharge.
- Logistics: Many top medical tourism providers include airport transfers, a dedicated case manager/translator, and assistance with finding long-term accommodation.
Conclusion: Your Next Step
The numbers are daunting, but they are manageable with the right strategy. You’ve done the hard work of seeking the truth about the cost. Now, let’s transform that knowledge into a plan.