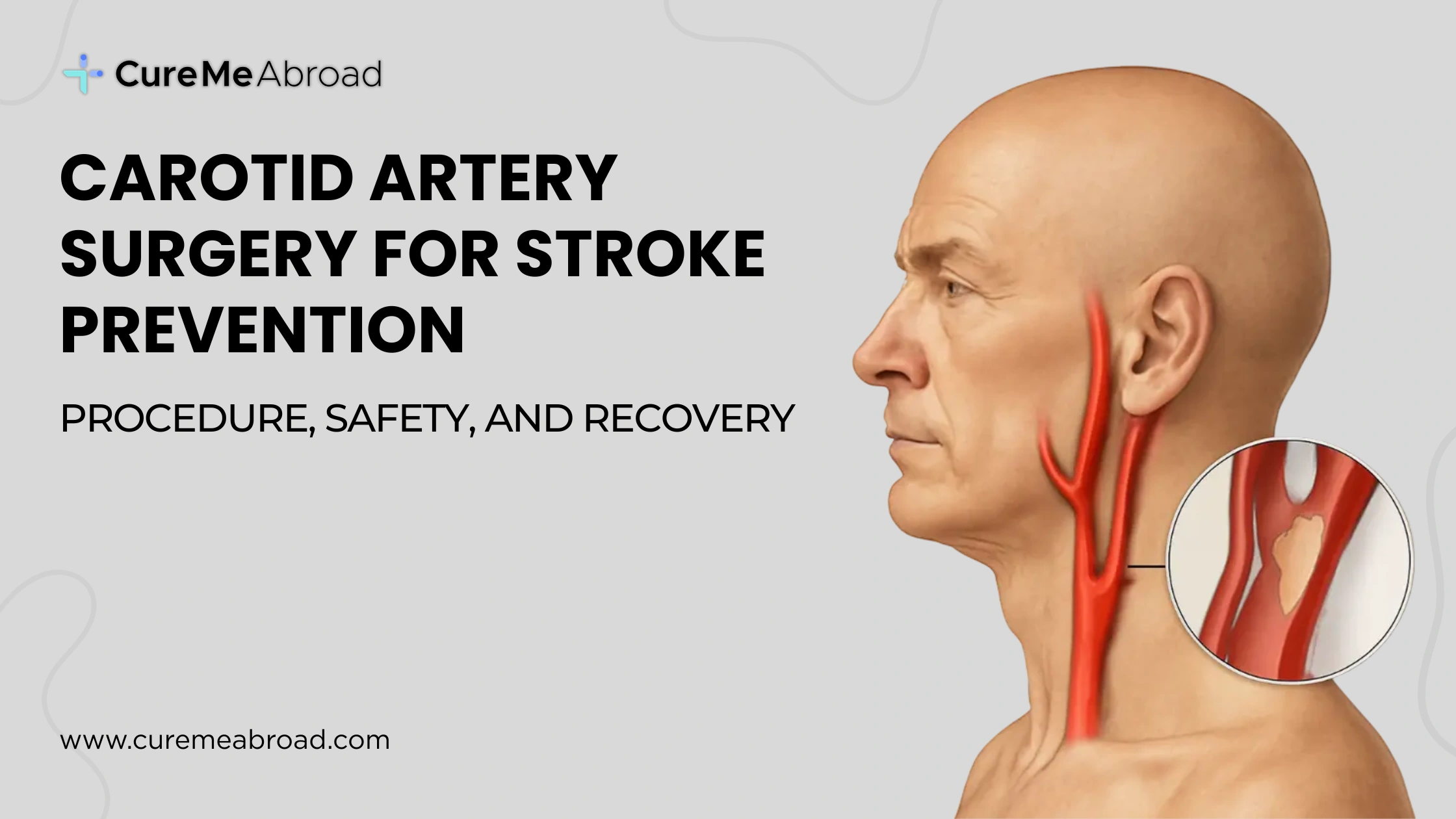
Stroke can happen suddenly, however, the majority of patients actually have a silently developing risk for stroke for many years. The most common reason for this is the narrowing of the carotid arteries, which are the main blood vessels that transport oxygen-rich blood to the brain. When these arteries are severely narrowed or blocked, the blood flow to the brain is decreased, thereby drastically the risk of stroke.
Surgery of the carotid artery is a preventive and sometimes life saving intervention, which makes the brain get a normal supply of blood and oxygen thereby helping in the reduction of the risk of stroke. Patients who have had symptoms such as transient ischemic attacks or minor strokes can benefit more if the surgery is done soon.
This article provides information for patients and caregivers about carotid artery surgery. It describes the reasons for the operation, its methods, preparation, and the usual recovery so that informed decisions can be made with confidence.
What is Carotid Artery Surgery?
Carotid artery surgery is of two types:
- Carotid Endarterectomy (CEA)
- Carotid Artery Stenting (CAS)
Carotid Endarterectomy (CEA)
Carotid Endarterectomy (CEA) is a surgical procedure used to treat disease of the carotid arteries. The large vessels to the brain that carry oxygen and blood are the carotid arteries. Here, the carotid arteries become narrower, reducing blood flow increasing the risk of stroke.
During the carotid endarterectomy, the surgeon will remove the accumulated plaques from the carotid artery surgically. The healthcare provider will make an incision, on the side of the neck where the plaques are accumulating inside the carotid artery. The healthcare provider will then open the artery and extract the plaques from it. The surgeon will then sew the artery closed. This will help normalize blood flow inside the head. The surgery is performed while the patient is conscious using local anesthesia or while sleeping using general anesthesia.
Carotid Artery Stenting (CAS)
Carotid Artery Stenting (CAS) is a medical operation in which a stent (a small, metal mesh tube) is placed inside to open a blocked artery. The stent is kept in the artery so that blood can flow to your brain more easily. In this way, the chances of having a stroke are reduced. The stent is not taken out; it stays there permanently. It functions as a frame that holds and maintains the artery open. Gradually, the artery recovers by growing around the stent.
During the procedure:
- A catheter is inserted from the groin or wrist
- A filter device is deployed to collect debris
- The constricted section is dilated with a balloon
- A stent is implanted to maintain the artery's openness
Why is Carotid Artery Surgery Performed?
The narrowing of the carotid arteries is most commonly due to atherosclerosis. This is where plaque builds up in the inner layers of the artery walls. The plaque is a combination of fatty matter, cholesterol, cellular debris, calcium, and fibrin. This is also known as "hardening of the arteries." It is known to affect the other arteries within the body too.
Carotid artery disease is just like coronary artery disease. In the latter, blockages occur in the cardiac arteries; this is likely to cause a heart attack. In the brain, it leads to a stroke.
Alternative treatment options are:
Just tests to check your carotid artery every year and no treatment. Cholesterol lowering medicines and diet. Blood thinning medicines to reduce your risk of stroke. A few of these medicines include aspirin, clopidogrel (Plavix), dabigatran (Pradaxa), and warfarin.
How to Prepare for Carotid Artery Surgery?
A Week Before
Before the operation, make sure to:, Inform your doctors about any allergies you may have.
Completely inform your doctors about all the drugs you are using. That includes both prescription and non-prescription drugs. It also includes vitamins, herbs, and supplements. Don't forget to let them know if you are taking blood thinners.
Follow doctor's instructions in making changes to your medicines. Some of the medicines the patient usually takes may have to be stopped.
The Day Before
Before having the operation, make sure to organize the patient’s trip back home immediately after the hospital stay. The patient should be driven home by an adult family member or friend after the hospital stay.
Observe strictly all the instructions given about fasting or abstaining from drinking before the procedure. If the patient is unsure, check with the doctor before taking any medicines.
Recovery: What is Expected After the Surgery?
At Hospital
After the operation, the patient is moved to a recovery area to allow thorough monitoring of the patient's vital signs. Only when it is confirmed that the patient's blood pressure, pulse, and breathing had stabilized within normal limits and the patient was awake, could the patient be safely transferred to the intensive care unit or a hospital room.
Eventually, the patient will be helped to get out of bed and encouraged to walk. Walking is a crucial process for better blood flow. If a drainage tube is close to the opening during the operation, the tube is generally removed the next morning. The patient will be put on liquids first and then allowed to have solid foods as tolerated.
Some level of discomfort and pain is to be anticipated after the intervention. The patient should only take pain meds as per the doctor's instructions. Unless it is a specific recommendation, the use of aspirin and some other pain killers should be avoided as they might lead to bleeding.
The doctor might arrange a few follow up duplex ultrasound examinations to see how the blood is flowing through the carotid arteries in the neck. Most patients are discharged within 1 to 2 days after a carotid endarterectomy.
At Home
As soon as they get home, the patient should ensure the incision site remains clean and dry. The doctor will give detailed instructions on bathing and caring for the wound. The stitches, if any, will be taken out in the follow up appointment. If adhesive strips were used, they must not get wet and normally they fall off on their own after a few days.
The patient may start eating normally unless the doctor advises otherwise. A cardiologist usually recommends a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, low, fat or non, fat dairy, whole grains, and lean proteins. One should avoid excessive consumption of processed, packaged, and high, fat foods.
Complications of Carotid Artery Surgery
TIA or Stroke: A temporary or permanent decrease in blood flow to the brain could happen during or after surgery, which could lead to strokes.
Bleeding: This can occur at the site of incision as well as, less commonly, within the brain.
Headache: There can be transient headache because of the alteration in the blood flow.
Seizure: Seizures may rarely occur due to altered cerebral blood flow.
Heart Attack: Existent patients with any heart problem can have a possible threat associated with heart issues.
Nerve Injury: Sometimes hoarseness of voice, paresthesia, or swallowing problems can ensue because of nerve damage.
Death: Rare, but potentially life-threatening complications have been reported in some individuals.
Complications are relatively rare, and a skilled surgical team does much to ensure their absence.
Cost Effectiveness of CEA vs CAS
An important aspect of cost is related to the complication risks that patients are expected to incur with the two procedures. These might contribute to added medical costs, and hence create a complex interaction of elements that determine cost-effectiveness. Elements such as rising complication risks due to age, costs related to drugs, and recurrence of stenosis can all impact the cost of both procedures, and therefore can have an important place in cost-effectiveness.
In clinical practice, the cost-effectiveness of carotid endarterectomy versus carotid artery stenting must be weighed against the individual differences in patients to ensure optimal outcomes. For long-term costs, at 10, 20, and 30 years, CEA generally resulted in lower costs to the patient. However, while CEA is often more cost-effective in the long term, CAS may be preferred in high-risk surgical candidates, such as those with severe comorbidities or unfavorable anatomy for open surgery. Besides, factors influencing the choice of the most cost-effective approach include patient age, degree of stenosis, and risk of embolic events.
Best Countries for Carotid Artery Surgery
Germany
The quality of the healthcare system and medical technology in Germany is world-class. The country is also at the forefront in medical research and development, which makes it the best place for advanced surgeries such as carotid artery surgery. The standard of quality in German hospitals and clinics is excellent as far as patient care is concerned.
Expertise in vascular surgery, which originated in Germany, is recognized around the globe. Most of these vascular specialists have sufficient experience and training from acclaimed medical institutions around the world. Though the price for carotid artery surgery in Germany is higher than that of other medical tourism countries, the standard of care and expertise of medical staff warrant this.
India
India has achieved considerable progress in the area of medical tourism, offering various treatments, such as carotid artery surgery. Indian healthcare facilities have earned experience in delivering high-class treatment, modern infrastructure, and well-trained healthcare staff. It can be said that the Indian healthcare industry is strictly controlled so that patients can get good treatment. The treatment cost for carotid artery surgery in India is significantly lower than in the West.
Mexico
Mexico is another popular international location for carotid artery surgery, and this is mainly due to patients from North America seeking treatment there. Mexico offers excellent medical standards at a significantly lower cost than that of the United States and Canada. Their hospitals have all modern facilities and most of their surgeons have trained elsewhere in the world for quality service delivery. The medical tourism industry in this country is quite established; many of its facilities have support services like bilingual staff and personalized care.
Turkey
Medical tourism in Turkey is a booming industry that offers a wide range of healthcare services at highly affordable rates. Among other things, the country has really put a lot of effort into healthcare development. It is recognized worldwide for its superb medical institutions, utilization of up- to- date medical technologies, and highly competent doctors.
Moreover, Turkish hospitals ensure the level of healthcare meets global standards and therefore patients can expect to receive quality treatment there. When you compare the cost of carotid artery surgery in Turkey and that in the Western countries, you will find a huge price difference in favor of Turkey. It is for this reason that foreign patients have been flocking to Turkey for various medical treatments.
Thailand
Thailand has become a premier destination for medical tourism due to its high-quality healthcare system and the availability of top, class surgeons. The nation provides the most advanced techniques in carotid artery surgery and is widely acknowledged as a center of excellence in vascular surgery. Medical institutions in Thailand not only have the most up-to-date medical equipment but also follow international healthcare standards.
One of the main attractions of having carotid artery surgery in Thailand is the dramatically reduced cost in comparison with Western countries. As a result, many patients choose this option. Alongside this, the country boasts a friendly and patient, oriented atmosphere, and most hospitals go the extra mile in providing medical tourism services such as travel arrangements, accommodation, and post-operative care.
Carotid artery surgery is essential in preventing strokes among patients who have severe narrowing of the carotid artery. It can greatly lessen the chances of devastating neurological incidents if done at the appropriate time and in the suitable patients.
Getting to know the operation, healing after surgery, the dangers involved, and the patient's commitments in the long run help him/her to be a part of the healing process. Surgery alone is not a cure. It is most effective when it is accompanied by ongoing medical care and good lifestyle habits.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is carotid artery surgery painful?
Patients generally suffer mild to moderate pain, which is easily managed with analgesics.
2. What is the duration of carotid surgery?
The time required for a carotid endarterectomy is normally between 1 and 2 hours.
3. When can I return to normal activities?
Light activities can be carried out in a few days. Full activity is normally possible within 2-4 weeks.
4. Can Carotid Artery Blockage recur?
Yes, it can. Restenosis can be prevented by lifestyle changes and drugs.
5. Is carotid surgery safe in elderly patients?
Age by itself is not a contraindication. Health is a stronger factor than age.
6. Will surgery stop all strokes in the future?
It lowers the risk of stroke caused by carotid artery disease, although it doesn’t eliminate all causes of stroke.